When selecting fiberglass materials for your next project, you may encounter two primary manufacturing methods: pultrusion and extrusion. While both processes create fiberglass products, they differ significantly in their approach and resulting characteristics. Understanding these differences is crucial to selecting the right material for your application.
In this article, you'll explore the key distinctions between pultruded and extruded fiberglass, including their production methods, physical properties, and ideal use cases. By the end, you'll have a clear understanding of which fiberglass type best suits your needs, ensuring optimal performance and longevity for your project.
Understanding Pultruded Fiberglass
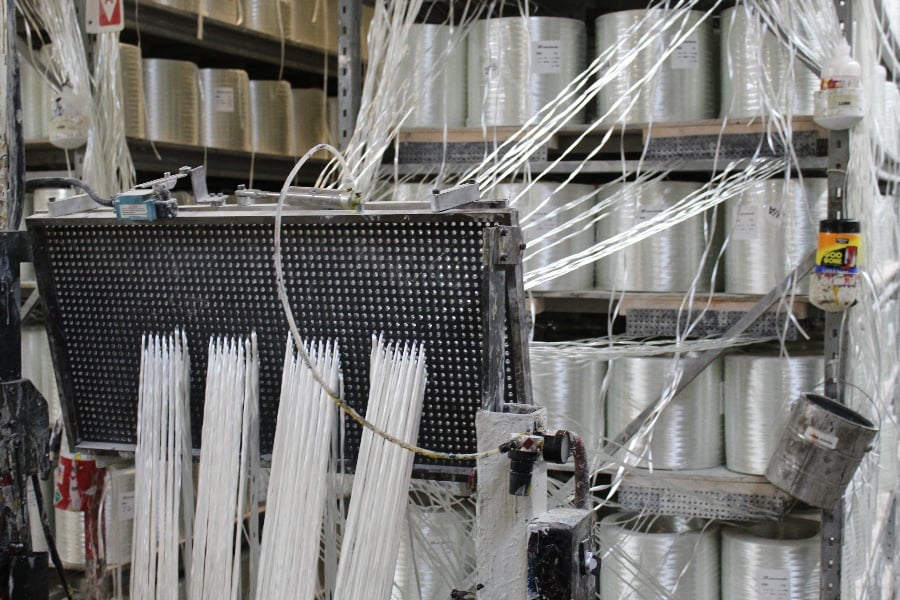
Pultruded fiberglass is a high-performance composite material produced by pultrusion. This method involves pulling continuous fibers through a resin bath so the resin adheres to the fiber surface and then through a heated die, which cures the resin to a non-reversible solid state, resulting in a strong, lightweight product with exceptional mechanical properties.
Key Characteristics
Pultruded fiberglass boasts several distinctive features that set it apart:
-
Strength-to-Weight Ratio: The continuous fiber reinforcement yields a product with a superior strength-to-weight ratio.
-
Dimensional Stability: The pultrusion process ensures consistent cross-sections along the entire length of the product.
-
Corrosion Resistance: The combination of fibers and resins creates a material highly resistant to chemical and environmental degradation.
Applications
Due to its unique properties, pultruded fiberglass finds use in various industries:
-
Construction: Used in structural components, bridges, and walkways
-
Electrical: Employed in insulators, cable trays, and utility poles
-
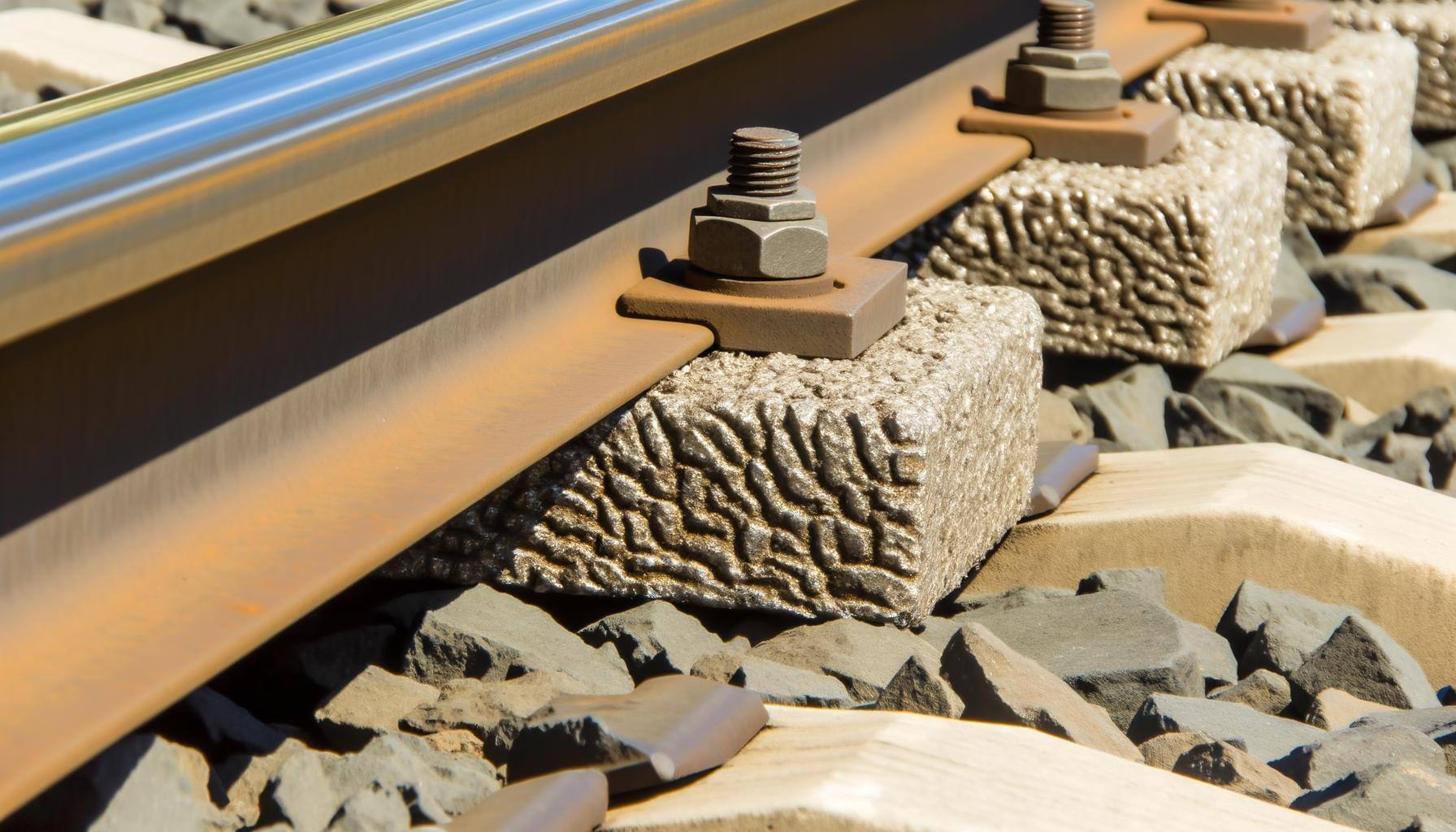
Transportation: Applied in automotive parts and railway components
Understanding the characteristics and applications of pultruded fiberglass is crucial when comparing it with other manufacturing methods, such as extrusion.
Exploring Extruded Fiberglass
The Extrusion Process
The extrusion process involves melting a thermoplastic material and forcing the liquid through an orifice to form the shape, and then holding that shape of the molten plastic while it is cooled to a solid.
Fiberglass can be included in this process in various ways. A braided or knitted fiberglass section can be inserted into the process, allowing molten plastic to form around it. Fiberglass can be added to molten plastics and then cut into small pieces to be re-melted in the extrusion process, and the mixed combination of fiberglass and molten resin can be fed through the shaping orifice to be cooled to a solid.
Other methods for forming molten plastic around fiberglass are also available.
Key Properties and Applications
Extruded fiberglass boasts several unique properties that make it suitable for various applications. Its lightweight, combined with good thermal insulation and electrical resistance, makes it ideal for construction and electrical applications. The material also exhibits excellent chemical and weathering resistance, enhancing its durability in controlled-temperature outdoor environments.
Compared to Other Fiberglass Types
While extruded fiberglass offers many benefits, it generally has lower strength-to-weight ratios than pultruded fiberglass. However, its manufacturing process allows for more complex shapes and profiles, making it versatile for applications requiring intricate designs.
The products are made from a plastic that softens and melts, so the choice of plastic depends on the operating temperature. Understanding these characteristics is crucial when selecting the right plastic and fiberglass type for specific projects.
Pultruded vs. Extruded Fiberglass: Key Differences Compared
When comparing pultruded and extruded fiberglass, several key differences emerge in terms of manufacturing processes, material properties, and applications. Understanding these distinctions is crucial to selecting the right fiberglass type for your specific needs.
Manufacturing Process
Pultrusion involves pulling continuous fibers through a resin bath and then a heated die, creating a uniform cross-section. In contrast, extrusion pushes molten material through a die, producing more flexible products.
Material Properties
Pultruded fiberglass typically offers superior strength-to-weight ratios and dimensional stability. Extruded fiberglass, while generally less strong and more temperature-sensitive, offers different flexibility and customization options.
Applications
Pultruded fiberglass excels in structural applications requiring high strength and corrosion resistance, such as bridge components and utility poles. Extruded fiberglass finds its niche in non-structural applications like window frames and decorative elements, where design flexibility is paramount.
By weighing these differences, you can make an informed decision on which type of fiberglass best suits your project requirements.
Conclusion
As you consider fiberglass options for your project, understanding the key differences between pultruded and extruded fiberglass is crucial. While both offer excellent strength-to-weight ratios and corrosion resistance, pultruded fiberglass excels in structural applications due to its superior strength and customizable profiles. Extruded fiberglass, on the other hand, shines in high-volume, standardized production scenarios.
By weighing factors such as required strength, production volume, and cost considerations, you can determine which process best suits your specific needs. Ultimately, both pultruded and extruded fiberglass have their place in modern manufacturing and construction, each offering unique advantages that can be leveraged to create innovative, durable solutions for a wide range of applications.