Have you ever wondered about the composition of fiber-reinforced resin composites, a material used in countless products you encounter daily? From automotive parts to sporting goods, fiber-reinforced resin composites are crucial in modern manufacturing.
This versatile substance combines the strength of fibers with the moldability of resins to create durable, lightweight composites. As you delve into the world of fiber-reinforced resin, you'll discover its complex makeup and the innovative processes used to produce it. Understanding its components and properties will give you valuable insight into its widespread applications and importance in various industries.
Understanding Fiber Reinforced Resin: What is It?
Fiber-reinforced resin, a crucial component in composite materials, is a versatile substance that combines strength with lightweight properties. This innovative material consists of two main elements: reinforcing fibers and a polymer resin matrix.
Composition of Fiber Reinforced Resin
Reinforcing fibers, typically made from materials such as glass, carbon, or aramid, provide the composite's structural integrity and strength. These fibers are embedded within a polymer resin matrix, which acts as a binder and protects them from damage.
Types of Resins Used
Common types of resins used in fiber-reinforced resin composites include:
Epoxy: Known for its excellent adhesion and chemical resistance and can be formulated for other specific properties.
Polyester: Offers good weathering properties. It can be formulated as cost-effective for a broad range of specific properties.
Vinylester: Similar to polyester with some possible weathering, chemical and toughness advantages.
Polyurethane: Can provide a performance, strength and cost advantage over other resins.
Specialty and hybrid resins can offer specific advantages for high-temperature use, increased fire resistance, long-life weathering, or other special requirements.
Applications and Benefits
Due to their exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, fiber-reinforced resin composites are used in various industries, from aerospace to automotive. This unique combination of properties allows for the creation of durable, lightweight structures that outperform traditional materials in many ways.
The Components of Fiber Reinforced Resin
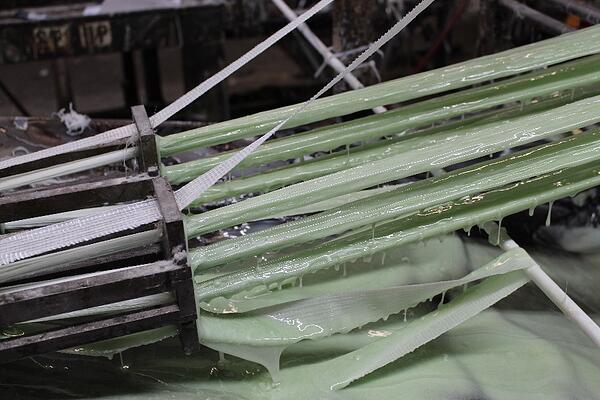
Fiber-reinforced resin is a versatile composite material consisting of two primary components: reinforcing fibers and a polymer matrix. These elements work synergistically to create a strong, lightweight material with diverse applications across industries.
Reinforcing Fibers
The backbone of fiber resin composites and reinforcing fibers provide strength and stiffness. Common types include:
Glass fibers: Offer excellent strength-to-weight ratio and affordability
Carbon fibers: provide superior strength and stiffness, making them ideal for high-performance applications where weight and size need to be reduced and conductivity is desired.
Aramid fibers: Known for their exceptional tensile strength, heat tolerance, and reduced weight, they are the best choice for applications where the highest strength with the lowest size and weight are both needed.
Basalt, plant-derived, and other man-made fibers can also offer some advantages of their own.
Polymer Matrix
The polymer matrix, typically a thermoset or thermoplastic resin, binds the fibers together and transfers loads between them. Popular matrix materials include those listed above as types of resin:
Epoxy, Polyester, Vinyl ester, Polyurethane, Specialty, and Hybrid
The specific combination of fibers and matrix determines the final properties of the fiber-reinforced resin composite, allowing for customization to meet various performance requirements in the aerospace, automotive, and construction industries.
Applications and Uses of Fiber-Reinforced Resin
Fiber-reinforced resin composites have revolutionized numerous industries due to their exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and versatility. These materials have widespread applications in the aerospace, automotive, marine, and construction sectors.
Aerospace and Aviation
In the aerospace industry, fiber-reinforced resin composites are crucial for manufacturing lightweight yet durable aircraft components. From fuselage panels to wing structures, these materials significantly reduce fuel consumption while maintaining structural integrity.
Automotive Engineering
Automotive manufacturers use fiber-reinforced resin composites to create high-performance vehicles with improved fuel efficiency. These materials are used in body panels, chassis components, and interior parts and offer enhanced strength and corrosion resistance.
Marine Applications
The marine industry benefits from fiber-reinforced resin's resistance to water and salt corrosion. Boat hulls, decks, and other nautical components are often constructed using these composites, ensuring longevity and performance in harsh maritime environments.
Construction and Infrastructure
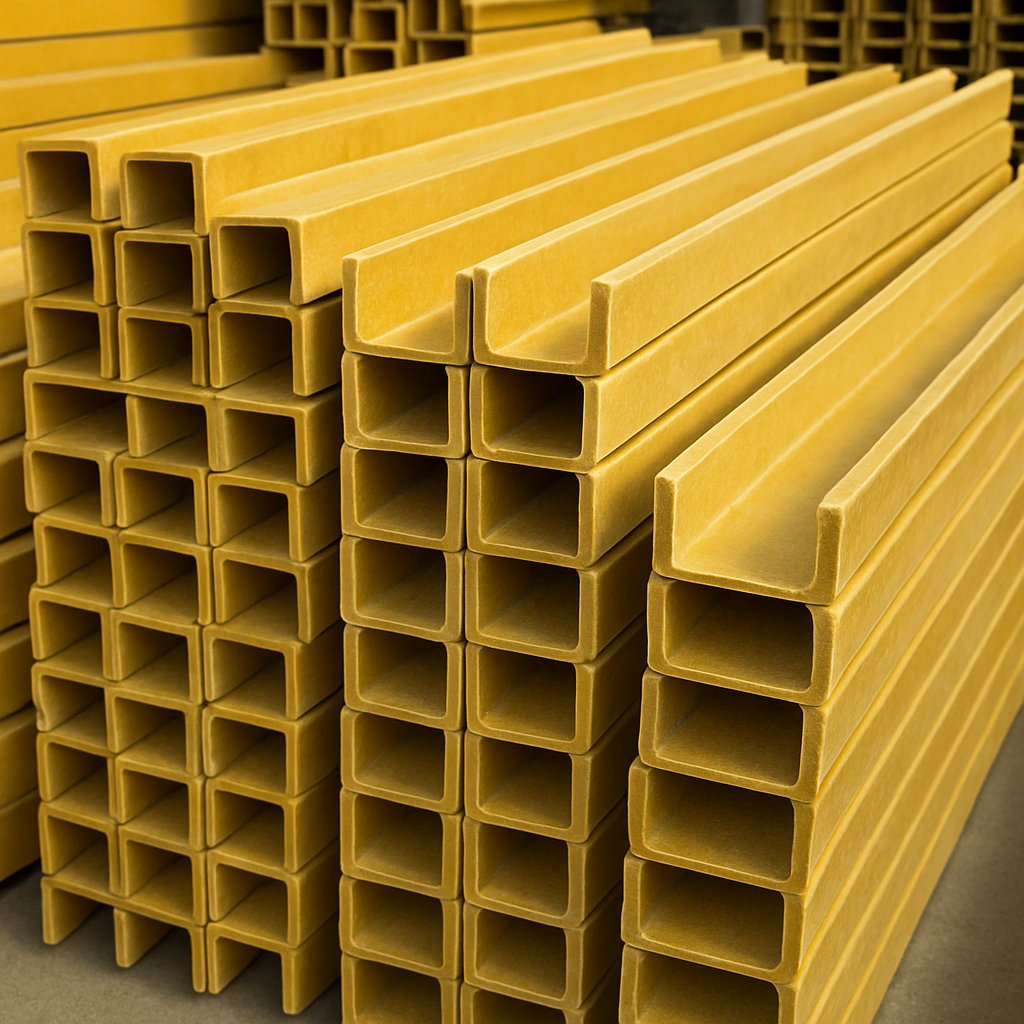
Fiber-reinforced resin composites are vital in modern construction, reinforcing concrete structures, bridges, and buildings. Their ability to be made fire resistant and durability and resistance to environmental factors make them ideal for long-lasting infrastructure projects.
Conclusion
As you've learned, fiber-reinforced resin is a complex material composed of reinforcing fibers embedded in a polymer matrix. The specific ingredients vary depending on the desired properties and applications but typically include synthetic resins, fiber reinforcements, and various additives. Understanding the composition of fiber-reinforced resin empowers you to make informed decisions when selecting materials for your projects.
Whether you're working in aerospace, automotive manufacturing, or construction, fiber-reinforced resin offers a unique combination of strength, durability, and versatility. By leveraging the benefits of this advanced composite material, you can push the boundaries of what's possible in your field and create innovative solutions for tomorrow's challenges.